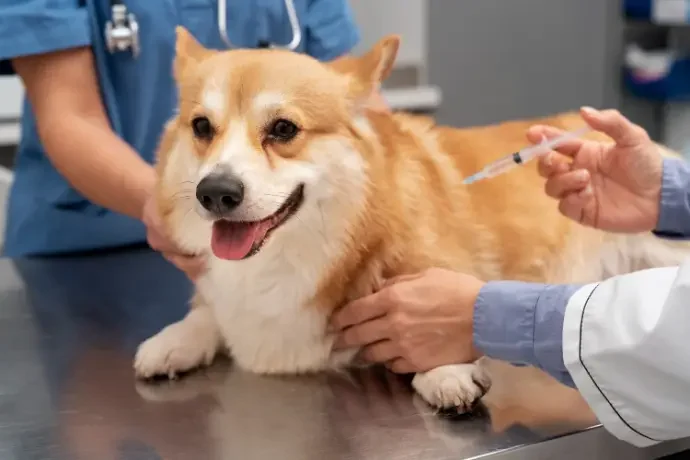
Why Veterinary Diagnostic Services Are Essential for Your Pet’s Health
As pets become more cherished members of the family, their health and well-being receive greater care than ever before. Modern pet owners understand that preventive care and frequent exams are critical to ensuring their furry pals live long, healthy lives. Advances in veterinary diagnostic services have made it easier to detect and treat health disorders at an early stage, lowering the risk of major sickness. This increased emphasis on pet health reflects a broader societal change toward recognizing pets as important members of the household, deserving the same amount of attention as any other family member.
What Are Veterinary Diagnostic Services?
Veterinary diagnostic services are specialist medical procedures and tests used by veterinarians to examine pet health and detect suspected illnesses or problems. These services entail the use of advanced instruments and procedures to detect underlying abnormalities that may not be seen during a routine physical examination.
Common veterinary diagnostic services include the following:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are used to analyze organ function, detect infections, and diagnose illnesses such as anemia or diabetes.
- Urine Analysis: Detect urinary tract infections, renal issues, or dehydration.
- Imaging Techniques: X-rays, ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs produce detailed images of bones, organs, and tissue.
- Allergy Testing: Determine which allergens are causing pain or reactivity in pets.
- Genetic Testing: Look for inherited disorders, particularly in certain breeds.
These veterinary diagnostic services are critical not just for identifying illnesses and infections but also for monitoring chronic disorders and ensuring that pets receive personalized therapies to maintain their health and well-being.
Importance of Early Disease Detection
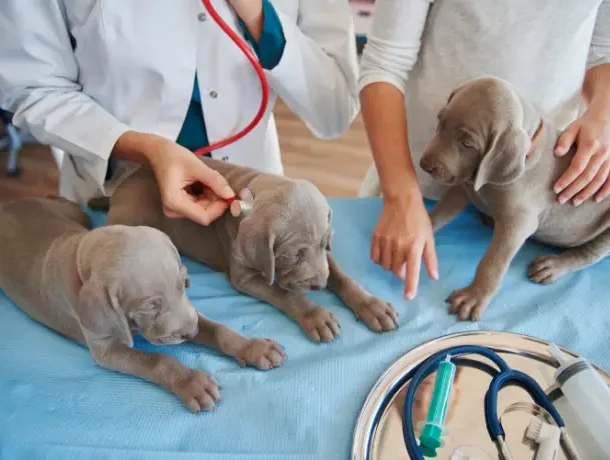

Early disease diagnosis is a cornerstone of modern veterinary treatment, ensuring that health problems in dogs are diagnosed and treated before they worsen. This proactive strategy has numerous significant benefits:
- Avoids Serious Health Complications: Identifying diseases in their early stages allows veterinarians to intervene quickly, preventing conditions from worsening or becoming life-threatening. For example, early identification of kidney illness or diabetes allows for more timely treatment and management.
- Reduces treatment costs: Treating advanced illnesses is frequently more expensive and complicated than treating them early. Regular diagnostic testing and veterinary checkups can help pet owners avoid costly emergency care by detecting problems early when treatment is simpler and less expensive.
- Enhances Quality of Life: Early disease detection allows dogs to receive appropriate care, reducing discomfort and anguish. This keeps them busy, happy, and healthy for longer.
- Extend Life expectancy: Pets recognized and treated early for common diseases such as heart disease or cancer live longer lives than those diagnosed later.
- Prevents Contagious Diseases: Early detection of infectious illnesses, such as parvovirus or feline leukemia, aids in preventing transmission to other animals in the family or community.
By adding routine examinations and veterinarian diagnostic services into a pet’s healthcare plan, owners can guarantee that their furry friends remain healthy, happy, and by their side for years to come.
Common Diagnostic Tests for Pets
Veterinary diagnostic services and tests are critical tools that assist doctors assess a pet’s health and identify any problems early on. Below are some of the most common diagnostic tests for pets:
1. Blood tests
A complete blood count (CBC) measures the number of red and white blood cells in the body, which can aid in the detection of infections, anemia, and immune system abnormalities. A blood chemistry panel assesses organ function, including the liver, kidneys, and pancreas, and detects diseases such as diabetes or renal illness.
2. Urine analysis
Offers insights about kidney and urinary tract health. Helps to detect infections, diabetes, and dehydration.
3. Diagnostic Imaging X-rays
Check bones, joints, and organs for fractures, cancers, or abnormalities. Ultrasounds provide comprehensive images of soft tissues, which aid in the detection of interior injuries or organ problems, CT scans and MRIs are used in more complex cases to evaluate neurological disorders, cancers, and internal injuries.
4. Fecal analysis
Identifies intestinal parasites, such as worms and protozoa detects gastrointestinal illnesses and abnormalities.
5. Allergy testing
Identifies environmental or food allergies that cause itching, rashes, or stomach difficulties.
6. Genetic tests
Screens for inherited diseases are found in specific breeds. Plans preventative care or treatment for breed-specific health hazards.
7. Heartworm testing
A simple blood test for heartworm infections, which can be lethal if untreated.
8. Skin Scrapings and Cultures
Identify skin diseases, mites, and fungal problems like ringworm.
These diagnostic tests serve an important part in maintaining a pet’s overall health, giving veterinarians the knowledge they need to identify and treat numerous problems. Regular testing helps pets live longer and healthier lives.
The Role of Routine Checkup
Routine checkups are an important aspect of keeping your pet’s health and well-being. Regular visits to the veterinarian are proactive actions to keep your pet healthy and receiving timely care. Here’s why regular checkups are important:
- Early detection of health issues: Routine checks frequently detect health issues before noticeable symptoms develop. Early veterinnary diagnosis services enables quick treatment, reducing complications and assuring better outcomes.
- Monitoring overall health: Veterinarians monitor your pet’s vital signs, weight, and overall condition throughout time. Changes in behavior, hunger, or physical condition can be addressed right away.
- Preventive Care: Vaccinations, parasite control, and dental cleanings are all essential components of regular checkups. These steps safeguard your pet against common diseases and conditions, such as disorders like heartworm or dental decay.
- Customized Health Plans: Checkups allow physicians to design individualized health regimens for your pet based on their age, breed, and lifestyle. Dietary, exercise, and medical care suggestions are tailored to help you maintain your best health.
- Strengthening the Bond Between Pet and Vet: Regular visits help your pet become accustomed to the veterinary setting, which reduces stress during sessions. A trusting relationship with your veterinarian leads to greater treatment and communication.
- Financial benefits: Routine checks can save you money in the long run by avoiding expensive emergency treatments or advanced procedures.
Prioritizing routine exams allows pet owners to take a proactive approach to their pet’s health. These checkups not only detect and prevent future problems but also lead to a longer, healthier life. Help your loved one live a longer, better, and happier life.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools and Technologies
Veterinary diagnostic services and medicine has made major advances in diagnostic tools and technologies, allowing veterinarians to provide more precise and efficient care to pets. These innovations enable early detection, accurate diagnosis, and targeted therapies, resulting in improved health outcomes.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Digital X-rays generate high-quality images for detecting fractures, cancers, and organ abnormalities. Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to visualize soft tissues, internal organs, and fluid buildup. CT scans (Computed Tomography) provide detailed 3D imaging for complex conditions including neurological problems or joint injuries. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, which are useful for identifying brain or spinal problems.
- Endoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure that employs a small camera to examine the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, or other interior systems. Useful for diagnosis Useful for diagnosing and treating problems that do not require surgery.
- Genetic Tests: Identifies genetic and breed-specific hazards.Helps pet owners and veterinarians develop preventive care regimens based on a pet’s genetic profile.
- Blood analyzers: Advanced in-clinic analyzers produce quick results for blood testing, allowing for the early detection of infections, organ problems, and other disorders.
- Molecular diagnostics: PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) testing can accurately detect specific pathogens or genetic alterations. Commonly used to diagnose viral infections and identify antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- Telemedicine and AI tools: Remote diagnostic tools and AI-powered platforms evaluate test and imaging data to give vets better insights.Telemedicine also enables virtual consultations and monitoring of continuing situations.
- Diagnostic wearables: Devices such as pet health monitors measure activity, heart rate, and other vital signs in real-time, providing vets and pet owners with valuable information.
These modern veterinary diagnostic services techniques and technologies have transformed veterinary treatment, making it more effective and accessible. By adopting these advancements, pet owners can ensure that their beloved companions receive the finest possible care, resulting in longer and healthier lives.
Choosing the Right Veterinary Diagnostic Services
Choosing the best veterinary diagnostic services is critical to your pet’s health and well-being. With so many options available, making an informed decision promotes correct diagnoses and effective treatment. Here are some important considerations to consider.
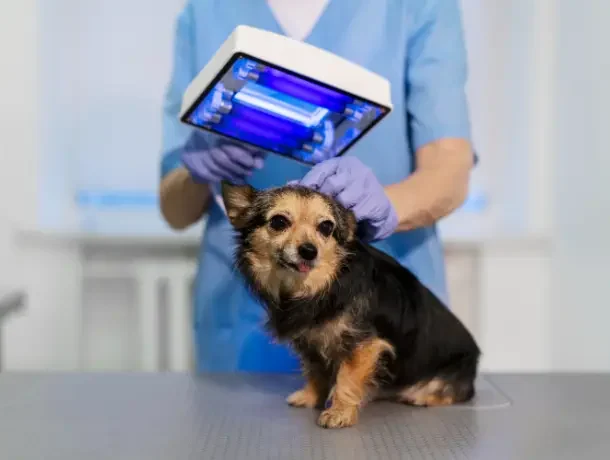

- Reputation and expertise: Look for clinics or facilities that employ trained and experienced veterinarians. Check online reviews and testimonials from other pet owners to get an idea of the service’s quality.
- Range of Diagnostic Services: Ensure that the facility provides a wide range of tests, including blood work, imaging (X-rays, ultrasounds), and advanced instruments like CT scans or genetic testing. A facility with extensive diagnostic capabilities can effectively handle a wide range of health conditions.
- Modern Equipment and Technology: Choose a service company that uses advanced diagnostic instruments to provide reliable results. Facilities equipped with cutting-edge technology can better detect and handle health risks.
- Personalized Care: Choose a service that focuses on individualized care, tailoring diagnostic and treatment programs to your pet’s specific needs.Communication and transparency are important characteristics of quality healthcare.
- Accessibility and Convenience: Consider the clinic’s location and operating hours to guarantee easy access in an emergency. Look for clinics that provide telemedicine services for consultations or follow-ups.
- Recommendations from your veterinarian: Your trustworthy veterinarian can offer valuable advice and propose reputable diagnostic services based on your pet’s health needs.
- Accreditation & Standards: Examine whether the facility meets industry standards and is accredited by relevant veterinary organizations. Accreditation assures adherence to quality and safety regulations.
By carefully considering these aspects, pet owners may choose a veterinarian diagnostic service that provides accurate, efficient, and compassionate care, ensuring their furry friends receive the finest possible health care.
Conclusion
Veterinary diagnostic services are an essential component of modern pet healthcare, providing crucial insights into your pet’s health and enabling early detection of any problems. These treatments, which range from routine checks to advanced diagnostic instruments, are critical to your pet’s health and long-term happiness.
Regular veterinary diagnostic services allow pet owners to treat health concerns, avoid serious complications, and enhance the bond with their beloved pets. Choosing the correct diagnostic services, coordinated by recognized veterinary professionals, ensures that your pet receives high-quality care that is personalized to their specific needs.
Put your pet’s health first today—a healthy pet is a happy pet!
Why Choose Vetscan Diagnostics ?
Expertise You Can Trust
Our veterinary laboratory team comprises experienced veterinary professionals specializing in biochemistry, microbiology, hematology, and histopathology.
Cutting-Edge Technology
We invest in state-of-the-art diagnostic technology, ensuring precision and efficiency in our tests. With the latest advancements at our disposal, we deliver timely and reliable results.
Early Detection, Lifelong Protection
Early detection is key to preventive pet care. Our comprehensive range of tests, from biochemistry to histopathology, is designed to catch potential health issues in their early stages.
Compassionate and Seamless Experience
Beyond expertise and technology, we pride ourselves on delivering a compassionate and seamless experience.